This topic is ONLY relevant to security gateways. It is NOT relevant to managed switches.
Left Navigation

Figure 1. Example Network Menu
The Configure section in the left navigation of the Central Management System (CMS) contains a Network menu (Fig. 1). This menu contains items for managing each of the local area network (LAN) interfaces for the selected Mako.
LAN Page
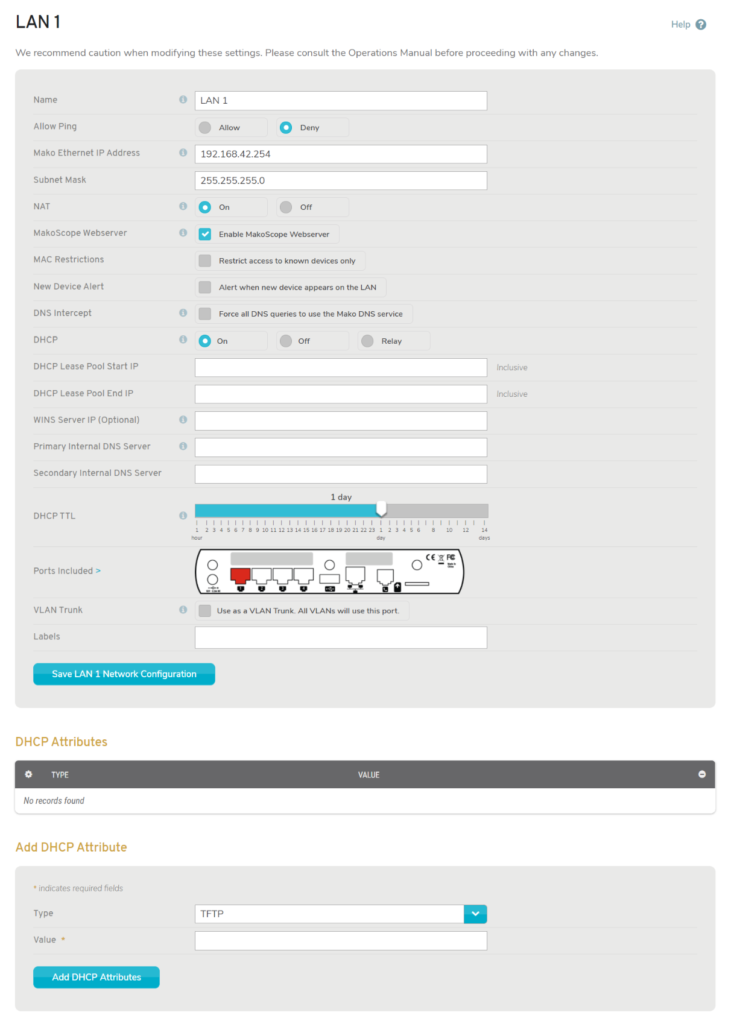
Figure 2. Example LAN Page
The LAN page (Fig. 2) provides settings for configuring your network. The page is the same for each LAN, however certain fields will show/hide based on the values in other fields.
Network Configuration
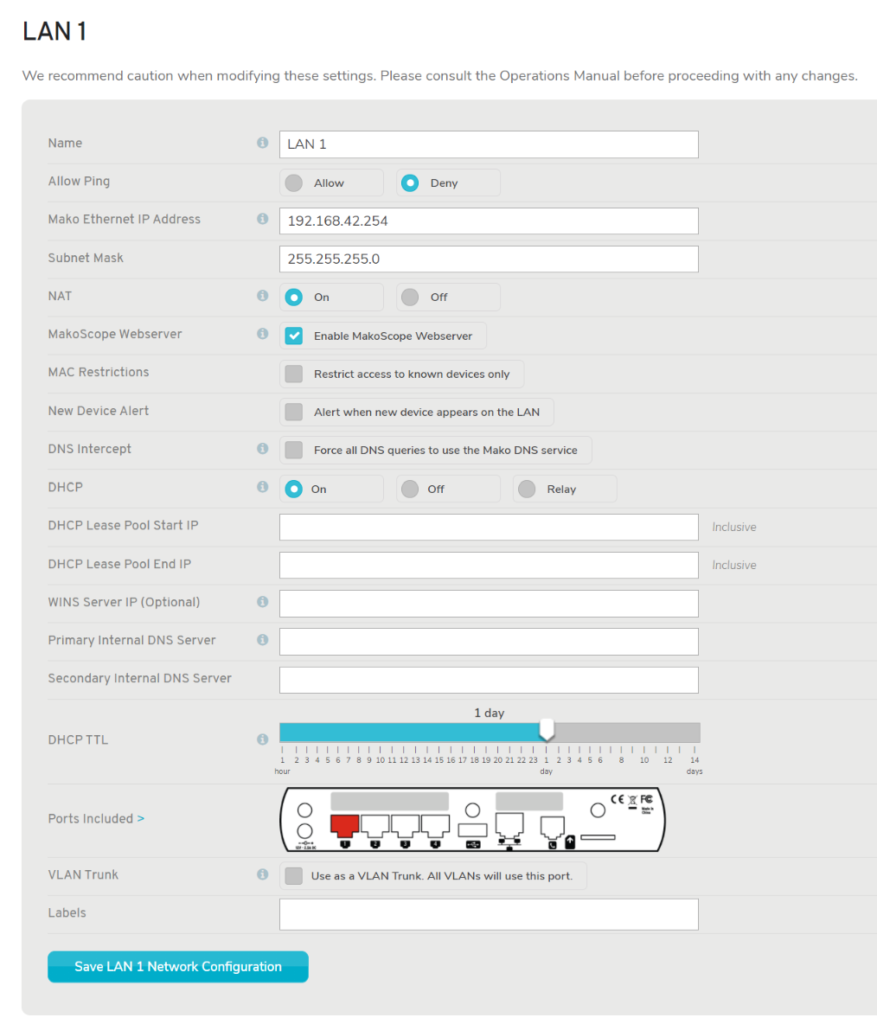
Figure 3. Example Network Configuration Form
The Network Configuration form (Fig. 3) contains the following fields:
Name
Enter a name for the LAN that is informative, memorable, and unique.
Allow Ping
The Allow Ping setting is set to “Deny” by default. If set to “Allow,” it will allow the LAN to respond to ping requests.
Mako Ethernet IP Address
Enter the internal IP address to be used by the Mako.
Subnet Mask
Enter the subnet mask for the internal IP address. This restricts the range of IP addresses available to a network. Many networks use a subnet mask of “255.255.255.0” to require the first three groups of digits to be identical for all IP addresses in the network, i.e. only the fourth set of digits varies.
NAT
Network Address Translation (NAT) allows you to place public IP addresses supplied by your Internet Service Provider (ISP) directly onto the LAN interface. The default value is “On.” Disabling NAT means IP traffic from devices attached to the LAN will not be modified by the Mako, and firewall rules will still need to be created to access these devices. Disabling NAT should only be done when using publicly routable IP addresses.
MakoScope Webserver
The MakoScope WebServer setting is enabled by default. This feature displays basic diagnostic and operating information for your Mako when you type its LAN IP address into a web browser. This information is only viewable if the web browsing device is also connected to the LAN.
MAC Restrictions
The MAC Restrictions setting is disabled by default. When enabled, it restricts LAN access to only known devices, i.e. a device must be registered in the system in order to use the LAN. To register devices, see the DHCP Leases documentation (even if the LAN does not use DHCP).
DNS Intercept
The DNS Intercept setting is disabled by default. When enabled, it forces all DNS queries from devices on the LAN to use the Mako’s built-in DNS service. Required for domain-based firewall rules to work correctly. See the Outbound Firewall Rules documentation for details.
DHCP
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) lets you centrally manage and automate the assignment of IP addresses on your network. The default value for DHCP is “On.”
If DHCP is set to “Off,” DHCP service will not be enabled for the LAN.
If DHCP is set to “On,” the following fields will be available:
DHCP Lease Pool Start IP & DHCP Lease Pool End IP
Enter the first and last IP addresses (Start IP and End IP, respectively) that define an inclusive range of IP addresses available for the LAN’s DHCP leases.
WINS Server IP (Optional)
If relevant for your network, enter the IP address of a WINS server, which is a Microsoft service that translates hostnames into IP addresses.
Primary Internal DNS Server
A Domain Name System (DNS) server is used to map domain names to IP addresses. Enter a primary DNS server in your network to handle your DNS queries.
Secondary Internal DNS Server
Enter a secondary DNS server in your network to handle your DNS queries in the event the primary DNS server is unavailable.
DHCP [Lease] TTL
Use the DHCP [Lease] TTL (Time to Live) slider to set the length of time before a DHCP lease issued to a LAN client expires. The default duration is 1 day, but this can be set to values ranging from 1 hour to 14 days. Move the slider left to decrease the duration or right to increase the duration. When the LAN client is assigned a new lease, it may be for a different IP address than the expired lease.
If DHCP is set to “Relay,” the following fields will be available:
DHCP Primary Relay Server
Enter a primary DHCP server external to the network that handles DHCP for the network.
DHCP Secondary Relay Server
Enter a secondary DHCP server external to the network that will handle DHCP for the network in the event the primary DHCP server is unavailable.
Ports Included
This image illustrates which of the Mako’s LAN interfaces (ports) have been assigned to the LAN you are configuring. Clicking the image or its label will take you to the Port Setup page. See the Port Setup documentation for more details.
VLAN Trunk
A Virtual LAN (VLAN) trunk is a port that handles traffic for all configured VLANs. VLAN traffic going across the trunk is tagged with the 802.1q VLAN ID. If you configure a port to act as a trunk, then all VLAN traffic will be carried over that port. Only one port at a time can be configured as a VLAN trunk.
If the VLAN Trunk checkbox IS checked, the following field will be visible:
VLANs Included
This displays a list of all VLANs. It includes VLANs configured on the VLAN Setup page as well as LANs with a VLAN ID set. Each VLAN in the list is a link to the appropriate page for managing the VLAN.
If the VLAN Trunk checkbox IS NOT checked for this LAN, but IS checked for a different LAN on the Mako, the following field will be available:
VLANs ID [Optional]
Enter an ID number to allow this LAN to act as a VLAN. Its traffic will flow through the VLAN trunk port like other VLANs. LANs with a VLAN ID set only have the VLAN ID tagged when going through the VLAN trunk, i.e. they are untagged on their normal ports.
Labels
The Labels field allows you to manage label values assigned to the LAN. A label can be added by typing a label value in the field and then pressing the Space bar on your keyboard. A label can be removed by clicking the minus icon next to the label.
Labels provide a way to apply firewall templates to LANs. See the Firewall documentation for more details.
Save Button
To save any changes made in the Network Configuration form, click the “Save” button.
DHCP Attributes
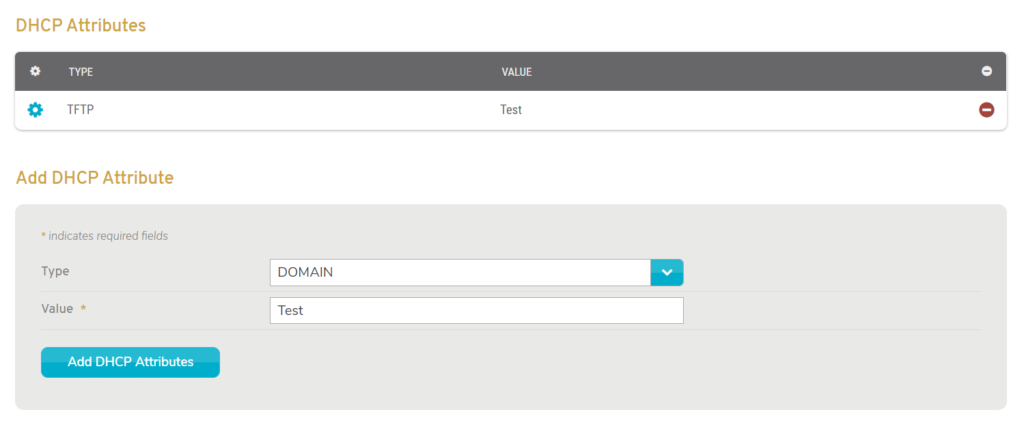
Figure 4. Example DHCP Attributes List and Add DHCP Attribute Form
If DHCP is set to “On,” you are able to view the DHCP Attributes list and the Add DHCP Attribute form (Fig. 4) for managing additional settings. This allows you to decide how you want various types of services to run by assigning them values that correspond to different actions and operations.
Add DHCP Attribute
To add a DHCP Attribute, choose an option for Type, enter an appropriate Value, and then click the “Add DHCP Attribute” button.
The Type dropdown initially contains the following services: TFTP, DOMAIN, and NTP Server.
The Value should correspond to the action or operation that you want the service to do.
After you add an attribute for a specific type, that type will no longer appear in the dropdown; it will appear in the list above the form instead. There it can be edited or deleted.
Edit DHCP Attribute
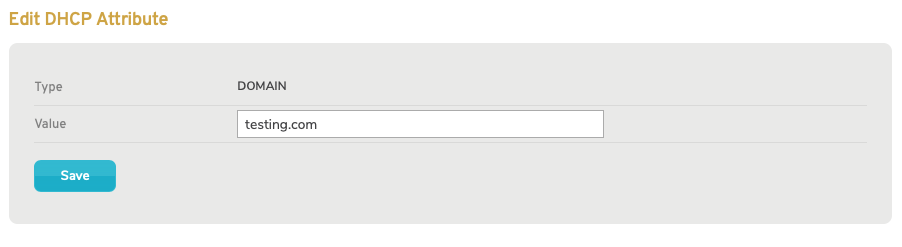
Figure 5. Example Edit DHCP Attribute Page
To edit a DHCP Attribute, click its gear icon button. This will open the Edit DHCP Attribute Page (Fig. 5) in a new window.
In the new window, you are able to change the Type and Value of the DHCP Attribute.
To save your changes, click the “Save” button. Then click the “X” icon in the header to close the new window, which will also refresh the attribute list to reflect your changes.
Delete DHCP Attribute
To delete a DHCP Attribute, click its minus icon button. This will delete the attribute from the list. The service for the deleted attribute will be available in the Type dropdown again.
