This topic is ONLY relevant to security gateways. It is NOT relevant to managed switches.
Overview
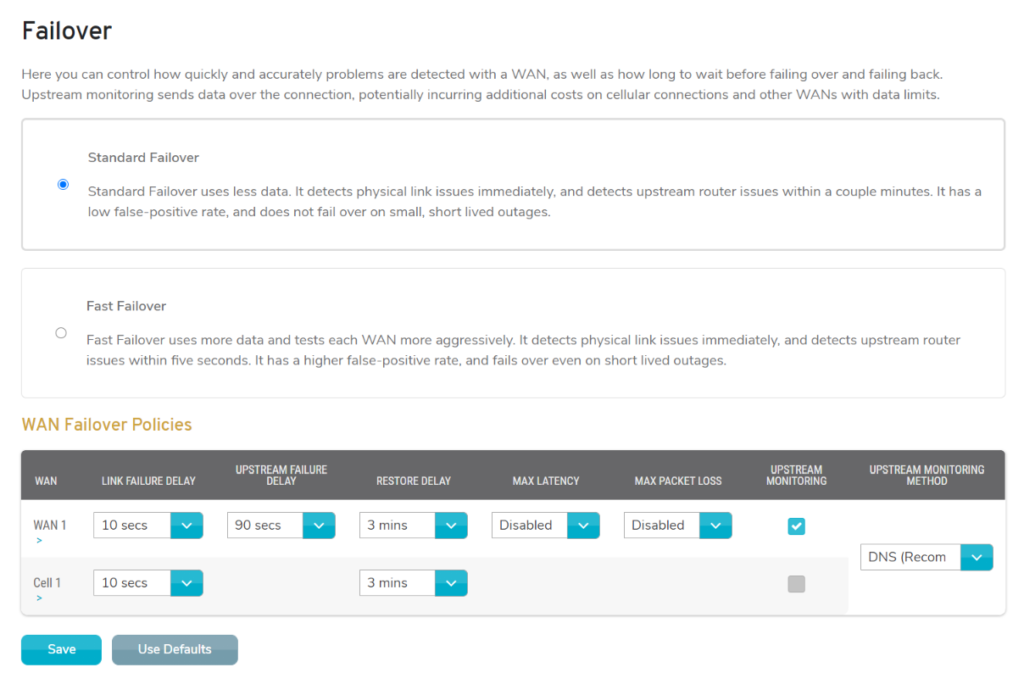
Figure 1. Example Failover Page
The Failover page (Fig. 1) allows you to control how quickly and accurately problems are detected with a WAN, as well as how long to wait before failing over and failing back. Upstream monitoring sends data over the connection, potentially incurring additional costs on cellular connections and other WANs with data limits.
Choose between two preset WAN failover policies (Standard Failover and Fast Failover), or create a custom WAN failover policy.
Preset WAN Failover Policies

Figure 2. Preset WAN Failover Policies
The preset WAN failover policies (Fig. 2) provide a quick way to configure failover with only a basic understanding of failover requirements. After choosing a preset option, the WAN Failover Policies form (Fig. 3) will be populated with the appropriate values for your selection. You must click the “Save” button to save the settings shown in the form.
Standard Failover
Standard Failover uses less data. It detects physical link issues immediately, and detects upstream router issues within a couple minutes. It has a low false-positive rate, and does not fail over on small, short lived outages.
This option is recommended for most sites.
Fast Failover
Fast Failover uses more data and tests each WAN more aggressively. It detects physical link issues immediately, and detects upstream router issues within five seconds. It has a higher false-positive rate, and fails over even on short lived outages.
This option is recommended for sites that cannot be down for 3-5 minutes when switching circuits during a failover event. This is for sites that need network traffic flowing within 10-15 seconds of a failover event. Risks include higher cellular usage.
Custom WAN Failover Policies
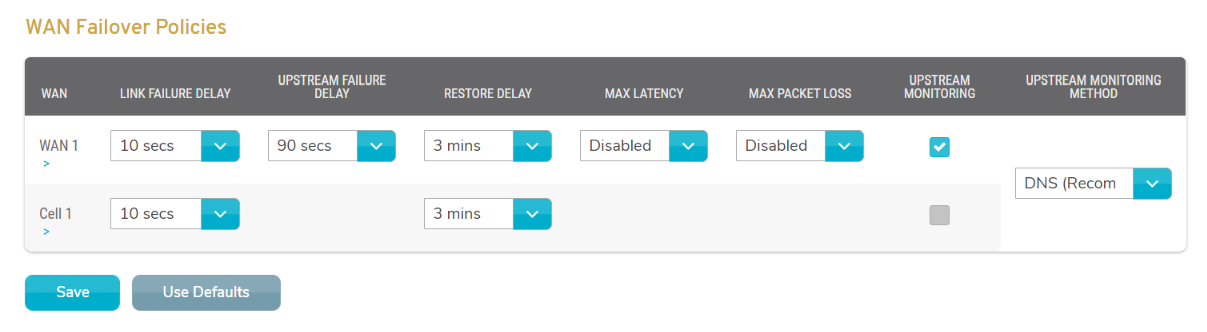
Figure 3. Example WAN Failover Policies Form
The WAN Failover Policies form (Fig. 3) provides a way to customize failover for users with a more advanced understanding of failover requirements.
The preset options should cover the majority of sites. It is not typically recommended to customize these settings.
WAN
The available WANs are shown as rows in the form. Each WAN has a link to its configuration page.
Link Failure Delay
Choose the time to wait after the physical connection has failed before trying to reconnect, e.g. the cable has been removed.
Upstream Failure Delay
Choose the time to wait after communication with the connection has failed before switching to the failover connection.
Enable Upstream Monitoring for the WAN to make this field available.
Restore Delay
Choose the time that the WAN must be up and stable before it can be used.
Max Latency
Choose a maximum threshold for latency on the WAN that will trigger a failover event.
Enable Upstream Monitoring for the WAN to make this field available.
Max Packet Loss
Choose a maximum threshold for packet loss on the WAN that will trigger a failover event.
Enable Upstream Monitoring for the WAN to make this field available.
Upstream Monitoring
Enable/disable upstream monitoring for the WAN.
Upstream Monitoring Method
Choose how upstream monitoring is performed for all WANs. Options are “DNS (Preferred)” and “HTTP.”
This single field applies to all rows in the form.
Save Button
Click the “Save” button to save the settings shown in the form.
Use Defaults Button
Click the “Use Defaults” button to reset the saved settings to match the Standard Failover preset option.
