This topic is ONLY relevant to security gateways. It is NOT relevant to managed switches.
Left Navigation
Figure 1. Example Internet Menu
The Configure section in the left navigation of the Central Management System (CMS) contains an Internet menu (Fig. 1). This menu contains items for managing each of the WAN and Cell Internet connections configured for the selected Mako.
In this example, we see “WAN 1” and “Cell 1” items. These items are listed in order of priority, as shown on the Summary page.
NOTE: the WAN and Cell management pages are similar but not identical. See the WANs documentation to manage a WAN connection.
Cell Page
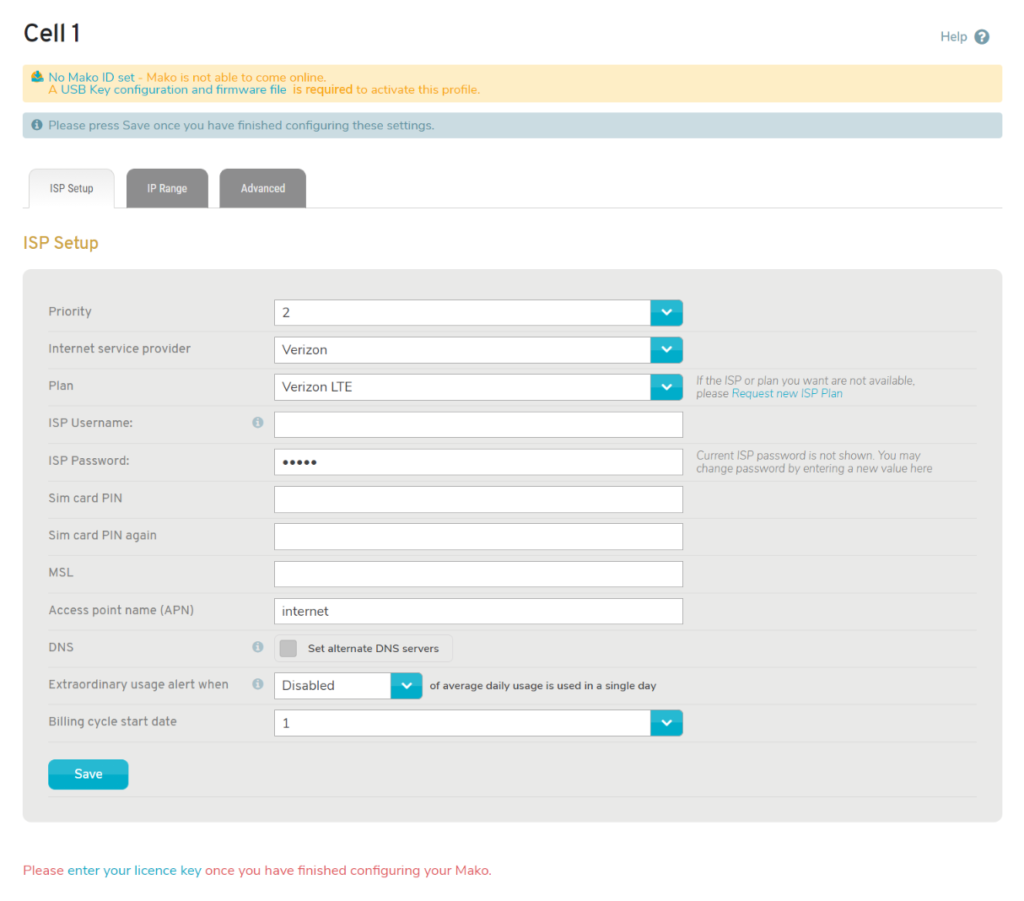
Figure 2. Example Cell Page
The Cell page (Fig. 2) contains three tabs of settings: ISP Setup, IP Range, and Advanced.
ISP Setup Tab
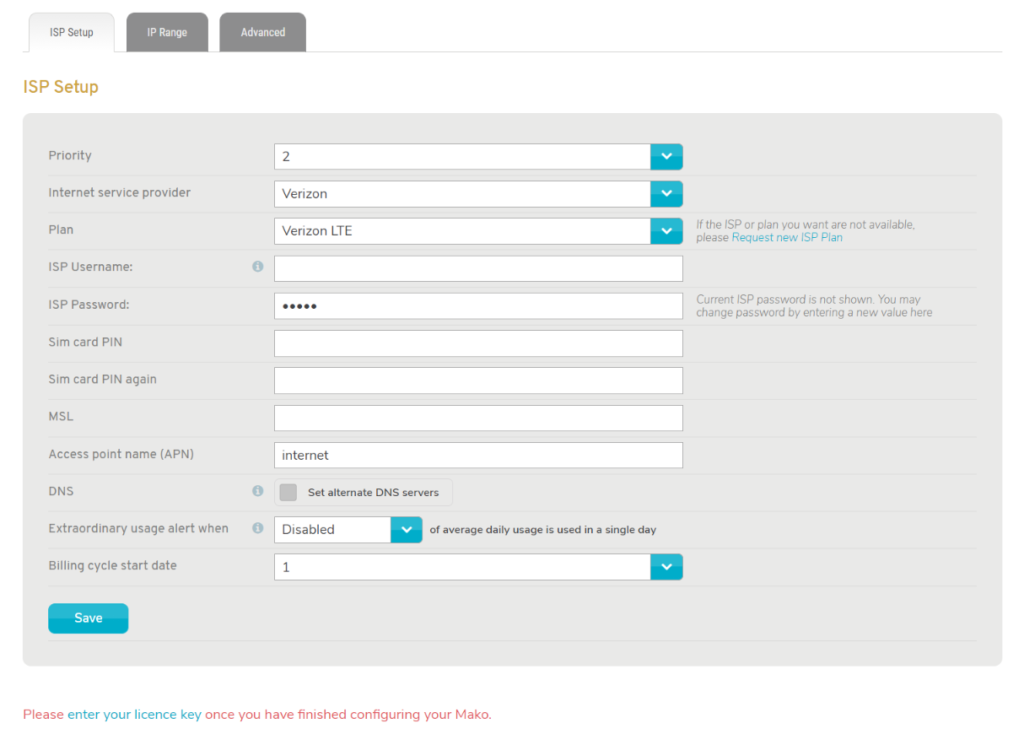
Figure 3. Example ISP Setup Tab
The ISP Setup tab (Fig. 3) allows you to configure the Internet Service Provider (ISP) for this Cell connection.
Priority
Select an option from the Priority dropdown to set the order in which the Mako will use this connection as compared to other connections. This can also be managed on the Summary page.
If the first priority connection is unavailable, the Mako will switch to the next connection in the priority list, and so on, until it reaches an available connection.
Internet Service Provider
Use the Internet Service Provider selector to choose your ISP vendor from a list of ISP vendors grouped by country.
Plan
Use the Plan selector to choose your ISP plan from a list of ISP plans offered by the ISP vendor you chose above.
ISP Username and ISP Password
If your ISP has provided credentials, enter them here.
SIM Card PIN
Enter and confirm the PIN number of your SIM card if you want to protect information associated with the SIM card.
MSL
Enter a Master Subsidy Lock (MSL) code if you want to lock your CDMA device. GSM devices do not use MSL codes for locking.
Access Point Name (APN)
Enter an APN if you want to use a specific gateway between your cellular network and another network, such as the Internet.
Set Alternate DNS Servers
A Domain Name System (DNS) server is used to map domain names to IP addresses.
If the Set Alternate DNS Servers checkbox IS NOT checked, then a standard DNS server will handle your DNS queries, which is the default behavior.
If the Set Alternate DNS Servers checkbox IS checked, then the following fields will be available:
Primary DNS
Enter a primary DNS server to handle your DNS queries.
Secondary DNS
Enter a secondary DNS server to handle your DNS queries in the event the primary DNS server is unavailable.
These two values are used by the Mako to query external DNS servers, which is only useful if you are using the Mako as a DNS server or have Mako Guardian enabled. Do not use DNS servers that are only reachable from a specific ISP or IP range.
Billing Cycle and Traffic Threshold Levels
Your selected ISP plan may trigger a set of optional fields here that allow you to further refine the behavior of your Mako based on the details of the plan. Below are some examples of these fields. This is not a comprehensive list.
Warning Threshold
Choose a percentage of your ISP plan data limit (from 50% to 100%) as the Warning Threshold. If data usage of the current billing cycle exceeds this threshold, it will trigger an alert.
Absolute Threshold and Absolute Threshold Status
Choose a percentage of your ISP plan data limit (from 50% to 410%) as the Absolute Threshold.
If data usage of the current billing cycle exceeds this threshold, the Absolute Threshold Status will be changed from “Monitoring” to “Blocking” automatically. This will block Internet access until either you set the status to “Ignoring” manually or the next billing cycle begins, which sets the status back to “Monitoring” automatically.
- Monitoring – data usage of current billing cycle HAS NOT exceeded Absolute Threshold.
- Blocking – data usage of current billing cycle HAS exceeded Absolute Threshold and Internet access is currently blocked.
- Ignoring – Internet access will not be blocked for the remainder of the current billing cycle, even if data usage exceeds Absolute Threshold.
Extraordinary Usage Alert When ___ of Average Daily Usage Is Used in a Single Day
If you want to receive an alert when data usage for a single day exceeds a certain percentage of the average daily data usage from the previous month, choose a percentage here.
Extraordinary Usage Alert When ___ of Free Usage Is Used in a Single Day
If you want to receive an alert when data usage for a single day exceeds a certain percentage of your free data usage for a billing cycle, choose a percentage here.
Billing Cycle Start Date
Choose the day of the month on which the billing cycle for your plan begins.
Failover Properties

Figure 4. Failover Properties
Clicking the “Failover properties” link (Fig. 4) will show/hide the following fields:
Failure Delay
Enter the time (seconds) to wait after the connection has failed before switching to the failover connection (the next connection in the priority list). The minimum value is 35 seconds.
Link Failure Delay
Enter the time (seconds) to wait after the connection has failed before trying to reconnect.
Restore Delay
Enter the time (seconds) that a network must be up and stable before it can be used. The minimum value is 35 seconds.
Secondary Healthy Test Period
Enter the time (seconds) between tests when the failover connection is healthy. The minimum value is 30 seconds.
Secondary Unhealthy Test Period
Enter the time (seconds) between tests when the failover connection is unhealthy. The minimum value is 30 seconds.
Enable HTTP Ping Monitoring
Check the Enable HTTP Ping Monitoring checkbox if you want to monitor connection health by periodically testing that a basic HTTP connection can be made. This may result in data usage and is not recommended for ISP plans with low data limits.
Save Button
To save any ISP Setup tab changes, click the “Save” button.
IP Range Tab

Figure 5. IP Range Tab
Cellular ISP plans do not support the use of IP ranges, so the IP Range tab (Fig. 5) does not allow you to manage IP ranges for Cell connections.
Advanced Settings Tab
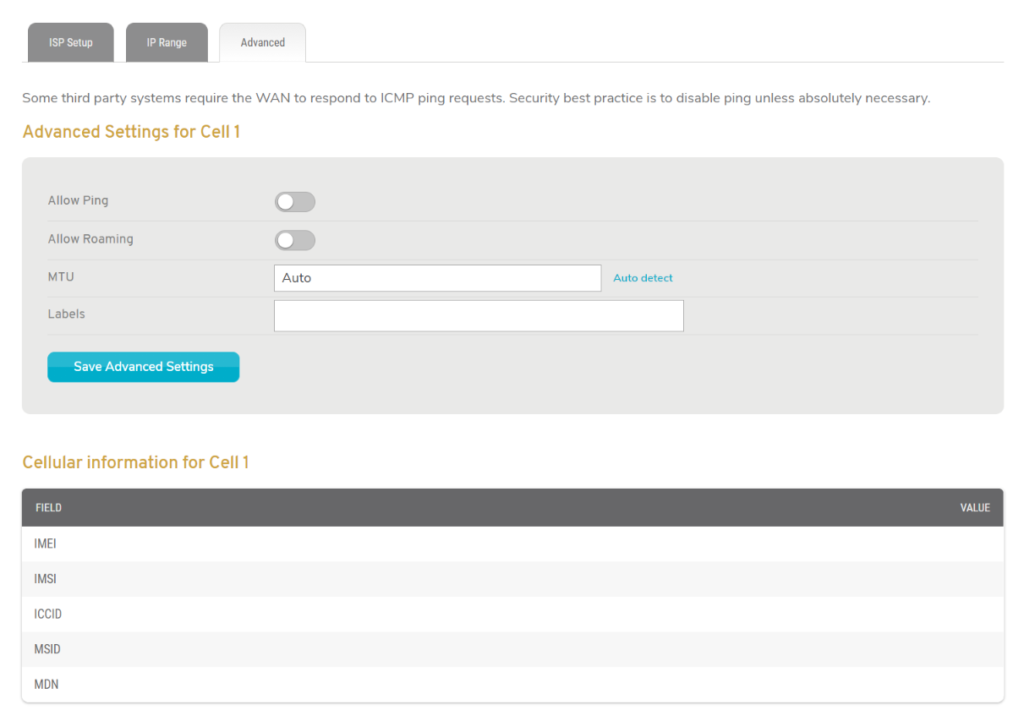
Figure 6. Example Advanced Settings Tab
The Advanced Settings tab (Fig. 6) allows for several options that you are less likely to need but may prove useful in some cases.
Allow Ping
The Allow Ping setting is disabled by default. If enabled, it allows the Cell to respond to Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) ping requests. Security best practice is to leave this disabled, however some third party systems require the Cell to respond to ICMP ping requests.
Allow Roaming
The Allow Roaming setting is disabled by default. If enabled, it allows the Cell to connection to operate when roaming. Enabling this may lead to unexpected carrier charges.
MTU
Here you can specify a Max Transmission Unit (MTU), which will limit the largest packet or frame size the selected Mako is able to send using the Cell. To set it, enter a numerical value. Alternatively, click the “Auto Detect” link to have the selected Mako use the MTU specified by the connected network.
Labels
The Labels field allows you to manage label values assigned to the Cell. A label can be added by typing a label value in the field and then pressing the Space bar on your keyboard. A label can be removed by clicking the minus icon next to the label.
Labels provide a way to apply firewall templates to Cells. There are also special labels that alter behavior when applied. For example, the “no-guardian” label will disable the Mako Guardian service for the selected Mako when this Cell is the default route. See the Firewall documentation for more details.
Save Button
To save any Advanced Settings tab changes, click the “Save Advanced Settings” button.
Cellular Information
A variety of identifying values are displayed in the Cellular Information panel.
IMEI
The International Mobile Equipment Identity (IMEI) is used to identify the mobile device.
IMSI
The International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) is used to identify the mobile user.
ICCID
The Integrated Circuit Card Identifier (ICCID) is used to identify the SIM card.
MSID
The Mobile Station ID (MSID) or Mobile Identification Number (MIN) is used to identify both the mobile device and its ISP.
MDN
The Mobile Directory Number (MDN) is the phone number associated with the SIM card.
